Key Features
-
Dynamic DNS Updates
Reacts in real time to scaling events, rolling updates, or resource deletions—keeping DNS entries accurate without manual steps. -
Flexibility & Control
- Manages DNS for LoadBalancer, NodePort, ClusterIP, and headless Services, as well as Ingress resources.
- Use annotation-based filters or custom FQDN templates to target specific records.
- Optionally ignore selected resources using annotation rules.
-
Broad Provider Compatibility
ExternalDNS integrates with the most popular DNS services, making it ideal for hybrid and multi-cloud deployments.DNS Provider Use Case Example Flag AWS Route 53 Public zones on AWS --provider=awsGoogle Cloud DNS GCP-managed domains --provider=googleAzure DNS Azure public DNS zones --provider=azureCloudflare External DNS management --provider=cloudflareDigitalOcean DNS DO-managed domains --provider=digitaloceanNS1, Infoblox, etc. Enterprise DNS solutions --provider=<name>
Architecture Scenarios
-
LoadBalancer
In cloud environments (AWS, GCP, Azure), ExternalDNS creates DNS A/AAAA records pointing to provisioned external IPs. -
NodePort / ClusterIP
Map DNS to node IPs plus NodePorts, or manage ClusterIP entries—even if they’re only internally routable. -
Headless Services
Assign stable DNS names to individual pod IPs (e.g., for Kafka or other stateful sets).
Installation
Add the ExternalDNS Helm chart and update:Ensure your cloud IAM role or API credentials have permissions to create and modify DNS records. See ExternalDNS GitHub for provider-specific requirements.
provider and provider-specific settings as needed:
You can also install ExternalDNS by applying a plain Kubernetes Deployment manifest—ideal for GitOps workflows.
Deployment Configuration
Below is a sampleDeployment manifest. Adjust args to fit your environment:
General Arguments
--source(service, ingress)--namespace(limit scope)--provider(aws, google, azure, cloudflare, etc.)--policy(sync or create-only)--domain-filter(restrict to specific domains)
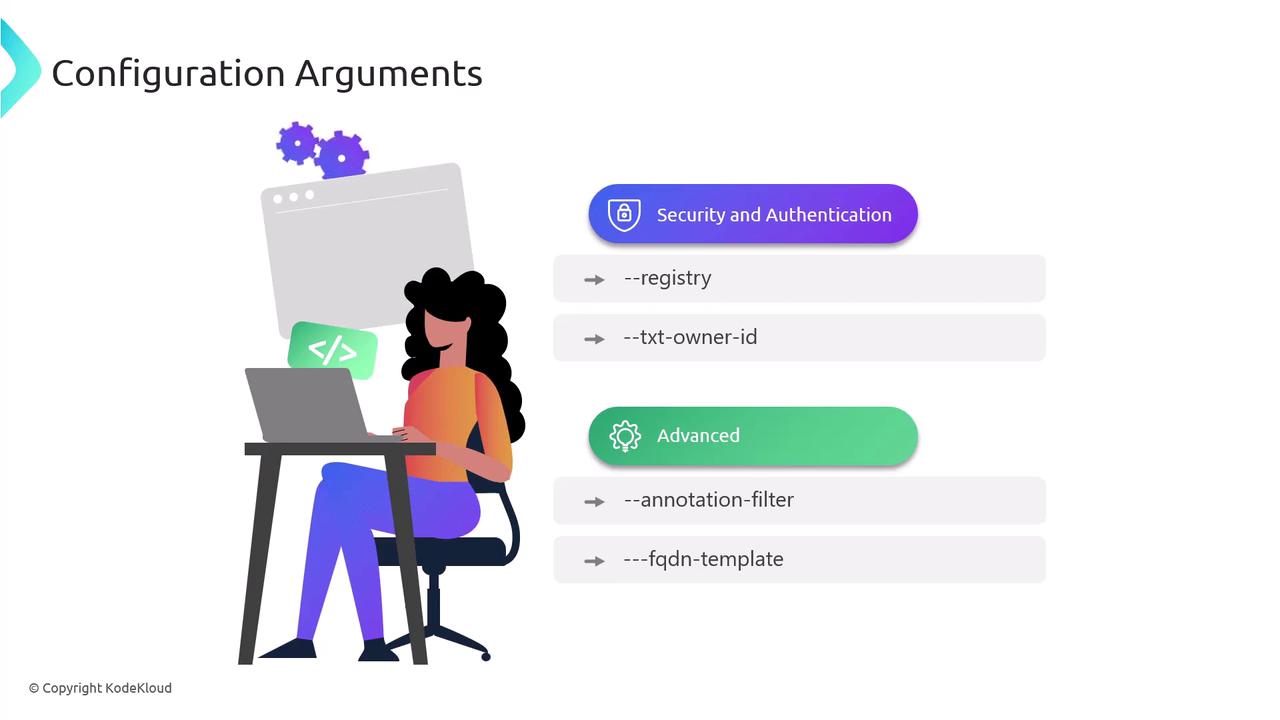
Security, Authentication & Advanced Options
--registry(txt, aws-tags)--txt-owner-id(unique TXT record owner)--annotation-filter(manage only annotated resources)--fqdn-template(custom FQDN generation)
Configuring Application Resources
ExternalDNS discovers resources via annotations. Add these undermetadata in your Service or Ingress:
Example: LoadBalancer Service
myservice.example.com, updating it if the external IP changes.
Now that you’ve explored ExternalDNS’s features, installation methods, and resource configuration, you’re ready to automate public DNS management for your Kubernetes workloads.